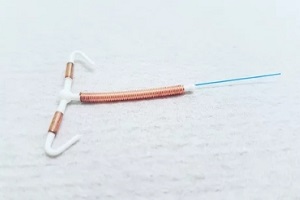
 Intrauterine devices, also known as IUDs, have become a popular form of long-acting birth control for many women. The copper IUD is one type that offers effective contraception without using hormones.
Intrauterine devices, also known as IUDs, have become a popular form of long-acting birth control for many women. The copper IUD is one type that offers effective contraception without using hormones.
It can prevent pregnancy for up to 10 years, making it a convenient and highly reliable option for many. However, copper IUDs do not suit every woman’s needs or health status.
Some key health conditions and risk factors may mean a copper IUD is not your best option.
Pregnancy
One of the main contraindications for a copper IUD is pregnancy. You should not have a copper IUD inserted if there is even the slightest likelihood that you might already be pregnant. Getting an IUD when you are pregnant can lead to serious, even life-threatening, risks.
The copper IUD works primarily by preventing the egg from being fertilized. The copper ions it releases create a toxic and inhospitable environment for sperm. However, it does not always prevent every single fertilization.
If an egg is fertilized shortly before or in the days after IUD insertion, the IUD could prevent proper implantation and growth. This could lead to you losing the pregnancy.
Having an IUD inserted while pregnant also drastically increases the risk of a dangerous infection called septic abortion.
Septic abortion is a severe uterine infection that can spread quickly to every area of your body. It requires immediate treatment with IV antibiotics and can lead to infertility or even maternal death in some cases.
To avoid risks to an existing pregnancy, you should always have a pregnancy test before getting a copper IUD. Inform your doctor right away if, since your last period, you have engaged in unprotected sex. You may need to reschedule the insertion until you can verify that you aren’t pregnant.
Gynecological Conditions
Several gynecological conditions may make a copper IUD less safe or effective. Certain disorders involving the uterus or cervix are generally contraindications for IUD use.
Abnormally Shaped Uterus
If you have an abnormally shaped uterus, such as one with large fibroids, inserting an IUD can be challenging or impossible. The IUD needs to fit properly inside the uterus to be effective. In some cases of uterine abnormality, the risk of the IUD being expelled is much higher.
Active Pelvic Infections
Active pelvic infections are another reason to avoid copper IUD insertion. Pelvic inflammatory disease, or PID, is one such infection. PID causes inflammation and infection of the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes.
 If you already have PID or another uterine infection, inserting an IUD could worsen the infection. The IUD insertion could “push” bacteria higher up into the pelvic cavity.
If you already have PID or another uterine infection, inserting an IUD could worsen the infection. The IUD insertion could “push” bacteria higher up into the pelvic cavity.
If you have had PID or any other uterine infection within the past three months following a pregnancy or miscarriage, it is best to wait. Your body needs time to fully recover before an IUD is placed.
Cervical or Uterine Cancer
Cervical and uterine cancers are also contraindications for IUD use. Localized cancers may be aggravated by IUD placement. Cancer treatments may make IUD insertion more complex as well. Discuss your cancer history thoroughly with your doctor.
Vaginal Bleeding
Unexplained vaginal bleeding should be evaluated before any IUD insertion. Bleeding could indicate an underlying gynecological condition that you need to treat first. Your doctor can run tests to identify the cause of bleeding and rule out problems such as cancer.
Pre-Existing IUD
Be sure to tell your doctor if you have a pre-existing IUD that has not been removed. Only one IUD should occupy the uterus at a time. Leaving multiple IUDs in place raises the risk of perforation and malposition.
Increased Infection Risk
Some people are more susceptible to developing infections related to an IUD. Those who get infections easily, have a weakened immune system, or have other medical conditions increasing infection risk should usually avoid copper IUDs.
The IUD insertion process and the presence of a foreign body in the uterus create susceptibility to bacterial growth. If you currently have PID or pelvic inflammation, the IUD could make it worse.
Those at high risk for PID, such as individuals with multiple sexual partners or STIs, must carefully consider the risks versus benefits of IUDs.
Proper preventative care, such as STI testing and treatment before insertion, can help reduce the chances of complications in higher-risk patients. Your doctor can help determine if a copper IUD is safe based on your specific infection and medical history.
Allergies
Though rare, some individuals are allergic to copper or other IUD components. Reported allergic reactions range from localized irritation to systematic anaphylaxis in sensitive individuals.
Nickel and polypropylene plastics are common sensitizers. If you have a known allergy to metals or medical implants, disclose this before proceeding with copper IUD insertion.
Signs of an allergic reaction might include unexplained rash, itching, swelling, or wheezing shortly after placement. Prompt medical care is needed if these occur.
Wilson’s Disease
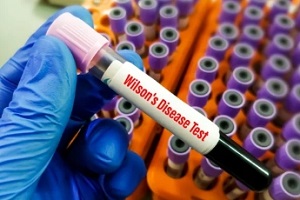 Wilson’s disease is a rare genetic disorder that causes excess copper to accumulate in the body’s tissues. Individuals with Wilson’s disease are advised to avoid additional copper exposure from an IUD, as it could exacerbate symptoms.
Wilson’s disease is a rare genetic disorder that causes excess copper to accumulate in the body’s tissues. Individuals with Wilson’s disease are advised to avoid additional copper exposure from an IUD, as it could exacerbate symptoms.
Your doctor can order testing for this condition if Wilson’s disease is suspected based on your health and family history.
Partner with Raleigh Gynecology & Wellness for Confident Copper IUD Choices
Deciding whether a copper IUD is right for you requires careful thought and an honest discussion with your doctor. While highly effective, the risks and side effects may make it less ideal for some situations. Fortunately, many other birth control options exist to explore if copper IUDs have too many contraindications for you.
Raleigh Gynecology & Wellness compassionate doctors provide personalized guidance on all forms of birth control. We consider your needs and goals to help you make informed choices for your health and body.
Contact us today at (919) 636-6670 or schedule an appointment online so we can help you determine whether a copper IUD is right for you.

 A
A  Mark your weekly patch change day on a calendar as a reminder and aim to change it at the same time each week.
Mark your weekly patch change day on a calendar as a reminder and aim to change it at the same time each week. Navigating your reproductive health means exploring many choices,
Navigating your reproductive health means exploring many choices,  From condoms and diaphragms to IUDs and vaginal rings, there are numerous ways that women can prevent unwanted pregnancy.
From condoms and diaphragms to IUDs and vaginal rings, there are numerous ways that women can prevent unwanted pregnancy. 
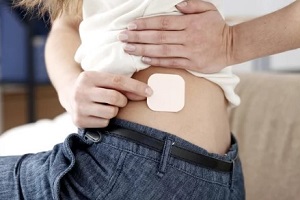 The
The  It is not recommended to place the birth control patch on your
It is not recommended to place the birth control patch on your  Regardless of where you choose to place your birth control patch, it will be necessary to check it regularly to ensure it remains in place. If it has become partially or fully detached and you are unable to reapply it, you should replace it with a new one right away. If the patch is no longer sticky, sticks to another surface or itself, or it has material stuck in it, you should start over with a new one.
Regardless of where you choose to place your birth control patch, it will be necessary to check it regularly to ensure it remains in place. If it has become partially or fully detached and you are unable to reapply it, you should replace it with a new one right away. If the patch is no longer sticky, sticks to another surface or itself, or it has material stuck in it, you should start over with a new one.
 If signs or symptoms of health risk or illness emerge before or during
If signs or symptoms of health risk or illness emerge before or during  The vaginal ring device is one of several types of prescription contraceptive that effectively reduces the risk of pregnancy. Similar with other contraceptive devices, vaginal rings are inserted for a prescribed period, yet the introduction of hormonal modification with this method can result in side effects.
The vaginal ring device is one of several types of prescription contraceptive that effectively reduces the risk of pregnancy. Similar with other contraceptive devices, vaginal rings are inserted for a prescribed period, yet the introduction of hormonal modification with this method can result in side effects.