 Taking charge of your reproductive health involves becoming aware of all the options available for preventing pregnancy until you’re ready. Raleigh OBGYN clinics provide in-depth counseling on a range of contraceptive methods to help you find the right solution aligned with your priorities and lifestyle.
Taking charge of your reproductive health involves becoming aware of all the options available for preventing pregnancy until you’re ready. Raleigh OBGYN clinics provide in-depth counseling on a range of contraceptive methods to help you find the right solution aligned with your priorities and lifestyle.
Barrier Methods: Blocking the Path to Conception
Barrier contraceptives work by physically preventing sperm from reaching and fertilizing an egg. They include:
Condoms
The male condom fits over the erect penis and collects semen to keep sperm from entering the vagina. Female condoms coat the inside of your vagina to block sperm. Both kinds also guard against STIs or sexually transmitted infections. But they can slip off or tear if they are misused.
Diaphragms and Cervical Caps
These soft, cup-shaped devices block the cervix, so sperm can’t enter. They need to stay in place 6-8 hours after sex. It’s advisable also to use spermicide cream to kill any sperm that may get past.
Hormonal Methods: Halting Ovulation and Altering Fertility Signs
Hormonal contraceptives use synthetic versions of naturally occurring estrogen and progesterone to stop ovulation. They also thicken the cervix’s mucus to inhibit sperm mobility and weaken the uterine lining to prevent implantation. Options include:
Oral Contraceptives
Also known as “the pill,” oral contraceptives contain synthetic variants of the hormones estrogen and progestin that naturally regulate the menstrual cycle. Combined formulations include both estrogen and progestin, while the progestin-only pill lacks estrogen.
When taken daily at the same time, these birth control pills work to inhibit ovulation and thicken the mucus in the cervix to prevent conception.
Oral contraceptives often provide non-contraceptive benefits as well, such as regulating menstrual cycles, reducing heavy bleeding, and improving acne. However, some women may experience side effects such as headaches, nausea, or small increases in blood pressure.
Injectable Contraceptives
Injectable contraceptives such as Depo-Provera provide a shot of the hormone progestin that lasts for three months at a time. The progestin works by preventing ovulation for the entire three-month period.
Many women appreciate only needing an injection four times a year. However, prolonged use may result in a decrease in bone mineral density since it stops estrogen production.
Implants
Implants are matchstick-size flexible rods that a Raleigh OB-GYN inserts under the skin of the upper arm. The implant rod steadily releases low doses of progestin over time and it is approved by the FDA for use up to 3 years. Nexplanon is the brand name for the implant.
Implants provide highly reliable long-acting contraception without needing to remember a daily pill. However, insertion and removal require a minor office procedure.
Patches and Vaginal Rings
 Contraceptive patches and vaginal rings deliver hormone doses through the skin or vaginal walls rather than orally. The patch sticks to the skin, similar to a Band-Aid, and is changed weekly. The soft ring is inserted into the vagina monthly.
Contraceptive patches and vaginal rings deliver hormone doses through the skin or vaginal walls rather than orally. The patch sticks to the skin, similar to a Band-Aid, and is changed weekly. The soft ring is inserted into the vagina monthly.
Both methods work by releasing estrogen and progestin. However, patches may cause skin irritation, and rings can slip out of place. Inconsistent use lowers the effectiveness of both options.
Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)
IUDs are small T-shaped devices positioned within the uterus that provide long-term contraception lasting 3-10 years, depending on the kind. IUDs work in various ways to prevent pregnancy:
Copper IUDs
The Paragard copper IUD triggers an inflammatory reaction and releases copper ions that damage sperm and eggs before they can unite, preventing fertilization. Approved for 10 years of use, it’s the longest-lasting reversible contraceptive option.
Hormonal IUDs
Hormonal IUDs such as Mirena, Skyla, or Liletta steadily discharge small quantities of the hormone progestin into the uterus for 3-8 years. Studies show Mirena remains highly effective for up to 8 years.
Permanent Sterilization Methods
Surgical procedures for women and men aim to permanently block fertility by interrupting the reproductive tracts:
Tubal Ligation
Tubal ligation involves cutting, tying, or sealing off the fallopian tubes to inhibit eggs from making their way from the ovaries to the uterus. It ensures sperm and eggs cannot unite.
The procedure is considered permanent birth control for women, as reversal attempts mostly fail or result in only partial restoration of fertility. Tubal ligation is done through either laparoscopy or mini-laparotomy as an outpatient surgery.
Patients can typically recover within a few days. Complications such as infection or damage to surrounding organs may rarely occur.
Vasectomy
A vasectomy is a quick outpatient procedure that cuts or blocks the vas deferens ducts that transport sperm. This prevents the release of sperm through seminal fluid during ejaculation.
Vasectomies are meant to be a permanent type of male contraception, but reversal is possible through a more complex microsurgery. Success rates for reversal procedures range between 30-90% in regaining fertility, depending on factors such as time elapsed since the original vasectomy.
Emergency Contraception
Emergency contraception can prevent pregnancy after having unprotected sex or if other birth control methods fail. Options such as Ella, Plan B, or Paragard IUD act before ovulation or fertilization can occur:
 Morning-after pills such as Plan B One-Step and Ella contain oral doses of progestin, estrogen, or anti-progestins that delay or prevent ovulation when taken within 72 hours of intercourse. They may also inhibit sperm migration or implantation.
Morning-after pills such as Plan B One-Step and Ella contain oral doses of progestin, estrogen, or anti-progestins that delay or prevent ovulation when taken within 72 hours of intercourse. They may also inhibit sperm migration or implantation.- Paragard copper IUDs can be inserted within five days of unprotected sex to prevent fertilization through copper’s spermicidal effects. Paragard is over 99% effective if inserted in time.
- Ulipristal acetate pill Ella is the most effective morning-after pill, staying potent for 120 hours after sex versus 72 hours for levonorgestrel tablets such as Plan B.
Raleigh Gynecology & Wellness Puts Reproductive Autonomy in Your Hands
Raleigh Gynecology & Wellness provides comprehensive contraceptive counseling, guiding you through choices aligned with your health status and future family plans. We want every patient empowered to manage fertility in ways that respect their life priorities and conscience.
Contact us today at (919) 636-6670 or online to discuss the full spectrum of pregnancy prevention solutions. Raleigh Gynecology & Wellness is here to help you take control over if and when you conceive so you can live life to the fullest on your terms.


 Endometriosis occurs when tissue similar to the uterine lining grows in other pelvic areas, such as the ovaries or fallopian tubes. The excess tissue thickens, breaks down, and bleeds monthly, causing inflammation, scarring, adhesions, and pain.
Endometriosis occurs when tissue similar to the uterine lining grows in other pelvic areas, such as the ovaries or fallopian tubes. The excess tissue thickens, breaks down, and bleeds monthly, causing inflammation, scarring, adhesions, and pain. Using oral contraception to regulate this hormonal often alleviates the intensity and frequency of these unpleasant episodes. Even lower dose formulations can reset your rhythm enough to rein in the radical highs and lows leading to problems.
Using oral contraception to regulate this hormonal often alleviates the intensity and frequency of these unpleasant episodes. Even lower dose formulations can reset your rhythm enough to rein in the radical highs and lows leading to problems.
 A
A  There are many hormonal contraceptive options to suit diverse needs and preferences. The pill offers flexibility but requires strict adherence. Methods such as the
There are many hormonal contraceptive options to suit diverse needs and preferences. The pill offers flexibility but requires strict adherence. Methods such as the 
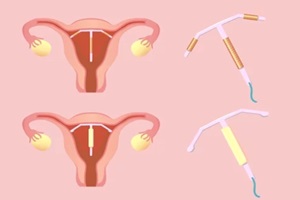 Making certain lifestyle tweaks during your initial recovery from an IUD insertion can optimize your progress and comfort.
Making certain lifestyle tweaks during your initial recovery from an IUD insertion can optimize your progress and comfort. Vitamin B1 – Also called thiamine, vitamin B1 helps regulate nerve signals and muscle contractions, which can ease persistent cramping. Typical dosing is 50-100 mg daily.
Vitamin B1 – Also called thiamine, vitamin B1 helps regulate nerve signals and muscle contractions, which can ease persistent cramping. Typical dosing is 50-100 mg daily. To avoid getting pregnant, an increasing number of women are turning to
To avoid getting pregnant, an increasing number of women are turning to  When considering the duration of contraceptive coverage, copper wins out over hormonal IUDs. A single copper IUD can protect from pregnancy for up to 10 years.
When considering the duration of contraceptive coverage, copper wins out over hormonal IUDs. A single copper IUD can protect from pregnancy for up to 10 years. Doing your homework on brands, dimensions, hormone levels, duration of use, and insertion procedures will shed light on the best selection for your comfort.
Doing your homework on brands, dimensions, hormone levels, duration of use, and insertion procedures will shed light on the best selection for your comfort.