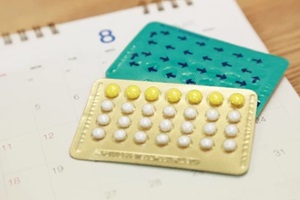
 The pill remains a popular and effective contraception option for many women. But combination birth control pills are not one-size-fits-all. Numerous formulations and choices are available depending on your health, preferences, and lifestyle.
The pill remains a popular and effective contraception option for many women. But combination birth control pills are not one-size-fits-all. Numerous formulations and choices are available depending on your health, preferences, and lifestyle.
What to Consider When Picking a Combination Pill
Your age and medical history matter when selecting a combination pill. Your doctor will review your health status, risk factors, and family history to recommend the safest options. For instance, if you’re over 35 and smoke, you may need to avoid pills with estrogen due to increased health risks such as blood clots.
Be sure to share all prescription and over-the-counter (OTC) medications you are on. Some antibiotics, seizure medications, and other drugs can interact with birth control and affect how well it works. Your doctor may suggest a different hormone dose or formulation to offset interactions.
How often you want to bleed is another key consideration. Some women prefer monthly periods for confirmation they aren’t pregnant. Others choose extended cycles or continuous dosing pills to limit bleeding to just a few times yearly. Discuss your preferences with your doctor.
If taking a daily pill on schedule seems challenging, opt for a method with more flexibility, such as the patch or ring. But if you already take daily meds and have an established routine, the pill may fit right in with minimal added effort.
Cost and insurance coverage often guide contraception decisions. Talk to your doctor about affordable options and potential copay differences between types. They can help find something budget-friendly based on your coverage. Look into savings programs from manufacturers, too.
Common side effects such as acne, weight changes, breakthrough bleeding, and breast tenderness should guide your birth control pick, too. If you’ve had unpleasant effects before, your doctor can recommend alternatives less likely to cause those reactions.
Also factor in your lifestyle – frequent travel, long or irregular work hours, intense sports or outdoor activities, etc. Choose a hassle-free pill that integrates smoothly into your normal routine. Opt for a non-daily contraception if your schedule varies.
Types of Combination Pills
There are a few main types of combination pills:
 Monophasic pills deliver equal quantities of estrogen and progestin in each active pill daily. These offer the most predictable bleeding patterns.
Monophasic pills deliver equal quantities of estrogen and progestin in each active pill daily. These offer the most predictable bleeding patterns.- Multiphasic pills vary hormone amounts across the cycle to mimic natural hormonal fluctuations. They may help minimize side effects for some women.
- Extended cycle pills limit withdrawal bleeding to just four times yearly by including more active pills and fewer inactive ones per pack.
- Continuous dosing pills provide hormones daily without any placebo pill breaks. This leads to fewer or no periods for some women.
Your doctor can review the options and help determine which pill schedule best suits your lifestyle and preferences.
Tips for Finding Your Match
Tracking your menstrual cycles, symptoms, moods, and preferences a few months before your visit provides helpful insight. Record details about your flow, pain levels, mood changes, and more to discuss with your doctor.
Be candid with your physician about all health conditions, even those that seem unrelated to contraception, such as migraines or depression—comprehensive information results in better recommendations.
Tell your doctor your ideal frequency of bleeding, feelings about taking a daily pill, and thoughts on synthetic hormone use. Share any past experiences with birth control side effects, too. Consider extended cycle or continuous dosing options if you want fewer or no periods.
If you’re new to the pill, start with a low or moderate estrogen dose formulation to minimize side effects as your body adjusts. After three months, reassess with your doctor if you need a different dose or formulation.
Use backup contraception such as condoms for the first seven days when starting a new combination pill until it becomes fully effective. Protection does not always begin immediately when starting the pill.
Give any new pill at least three months for potential side effects such as nausea, headaches, or spotting to resolve before switching. Some symptoms subside after your body gets used to it.
Set a daily reminder on your phone to take your combination pill at the same time. Consistency is key for effectiveness. Consider pairing it with another part of your routine, such as brushing your teeth, so it becomes a habit.
When to Re-Evaluate Your Combination Pill
See your doctor promptly if you start any new medications, as drug interactions may reduce birth control effectiveness. Your physician can confirm the pill remains suitable or recommend alternatives if needed.
Developing new health conditions such as high blood pressure, heart disease, or migraines with aura also warrants discussing whether to adjust your birth control plan. Your risks and options may change.
Women over 35 who smoke face higher health risks on estrogen-containing combination pills such as blood clots. Your doctor may advise a progestin-only pill, IUD, or other method instead.
 Prolonged immobility after major surgery, childbirth, injury, or serious illness may mean pausing combination pills temporarily due to increased clot risks. Discuss this with your physician.
Prolonged immobility after major surgery, childbirth, injury, or serious illness may mean pausing combination pills temporarily due to increased clot risks. Discuss this with your physician.
Persistent or intolerable side effects such as severe mood changes, headaches, or nausea are signs it may not be the ideal pill for you. Make an appointment to explore other formulations or methods better suited to your body.
Customize Your Combination Birth Control with Raleigh Gynecology & Wellness
There’s no one-size-fits-all birth control pill. Women have unique medical backgrounds, priorities, and ways of life that determine what works best. That’s why thoughtful one-on-one consultations are valuable for weighing the different formulations against your health history and personal preferences.
If you are uncertain about the best option or want a second opinion, please know that my compassionate team at Raleigh Gynecology & Wellness is always here.
Contact us today at (919) 636-6670 or schedule a consultation online, and our team will listen and guide you through all available options to discover your ideal match.

 The
The  Hormones affect practically everything in the female body. When they are imbalanced, you feel it. Conditions such as
Hormones affect practically everything in the female body. When they are imbalanced, you feel it. Conditions such as 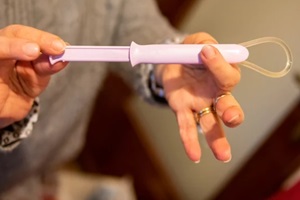 Having a history of migraines, blood clots, strokes, heart attacks, liver disease, or
Having a history of migraines, blood clots, strokes, heart attacks, liver disease, or 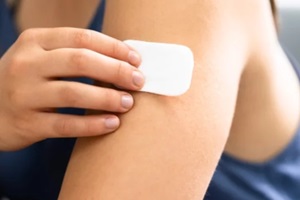 The
The  Your blood levels of both hormones stay within this target range all week long with the patch. There are no significant ups and downs.
Your blood levels of both hormones stay within this target range all week long with the patch. There are no significant ups and downs.
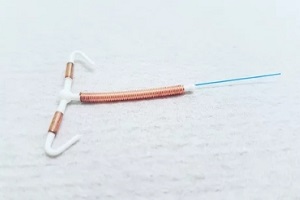 Hormonal IUDs such as Mirena, Kyleena or Skyla can lighten periods or lead to no period at all. On the other hand, the nonhormonal
Hormonal IUDs such as Mirena, Kyleena or Skyla can lighten periods or lead to no period at all. On the other hand, the nonhormonal  The
The  Rinse the ring in cool water and reinsert it as soon as possible if It’s been out for less than 3 hours.
Rinse the ring in cool water and reinsert it as soon as possible if It’s been out for less than 3 hours.