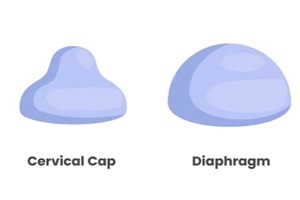
 Barrier methods such as condoms, diaphragms, cervical caps, and spermicides can provide effective protection against pregnancy when used properly.
Barrier methods such as condoms, diaphragms, cervical caps, and spermicides can provide effective protection against pregnancy when used properly.
Follow these tips and tricks to select the best barrier methods for your needs, use them correctly every time you have sex, and know what to do if mistakes happen.
Understand All the Barrier Options Available
The first step to using barrier contraceptives effectively is understanding exactly what they are and the various options to choose from.
Barrier methods work by physically blocking sperm from entering the uterus and reaching an egg. Some also protect against sexually transmitted infections.
Types of barrier methods include:
- External or “male” condoms fit over the erect penis to catch semen, preventing sperm from entering the vagina.
- Internal or “female” condoms are pouches inserted in the vagina before sex. The inner ring anchors the condom behind the pubic bone, while the outer ring stays outside the vaginal opening.
- Cervical barriers, such as a diaphragm, cervical cap, or contraceptive sponge, block the cervix, so sperm can’t pass through.
- Spermicidal gels, foams, creams, films, and suppositories kill sperm trying to make their way past the vagina.
Find the Method that Fits Your Anatomy
Getting the right size is essential for cervical barriers such as diaphragms and caps that block the cervix. See a healthcare provider for a fitting to determine the product with the best anatomical match.
One-size diaphragms may work for those who haven’t given birth. The vagina changes shape during arousal, so you might try different sizes of internal condoms to see what feels most secure during sex.
External condom brands vary in shape and width, so explore to find the best fit for you and your partner.
Trying a few kinds helps ensure you have condoms that feel good and stay put. Check the package before unrolling on the penis.
Learn to Insert and Use Barriers Correctly
Following the exact usage instructions every time you have sex ensures your barrier method works effectively. Common mistakes make pregnancy or infection more likely.
For condoms, pinch the tip while rolling onto the erect penis to leave extra space at the end to collect semen. Smooth out any air bubbles.
Apply water- or silicone-based lube to prevent breakage. After ejaculation, grip the base of the condom as you withdraw to keep it from slipping off.
 Always apply spermicidal gel before inserting a diaphragm, cervical cap, or sponge. Check that the barrier method completely covers your cervix before and after sex by feeling with your finger.
Always apply spermicidal gel before inserting a diaphragm, cervical cap, or sponge. Check that the barrier method completely covers your cervix before and after sex by feeling with your finger.
Leave barriers in place for the recommended time after sex before removal. First, wash your hands when using spermicidal film, suppositories, or tablets.
Insert the spermicide close to your cervix several minutes before intercourse. Apply additional doses if needed per the product instructions.
Discuss Barrier Use with Your Partner(s)
Having an open, honest conversation with your partner makes it more likely you’ll both use the barriers correctly and consistently.
Discuss the reasons barrier methods matter for preventing pregnancy or sexually transmitted infections.
Agree that you’ll always use the barriers during sex and foreplay. Talk about how you’ll put them into place for times of intimacy.
Troubleshoot any awkwardness or discomfort. Address what you would do in case of problems such as slipping, breakage, or other mistakes. This builds trust and accountability.
Consider Using a Backup Method
No single birth control method is 100% reliable with real-world use. Using a second, non-hormonal barrier method provides extra pregnancy prevention and STI protection.
Try pairing condoms with a diaphragm, cervical cap, or spermicidal gel. The condoms protect against infections, while the other method provides backup contraception.
Dual barrier use lowers the risk of user error, slippage, or breakage. If one fails, you still have pregnancy protection.
Get Tested for STIs Regularly
While barriers reduce STI risk, they can’t prevent transmission in every scenario. Use condoms properly every time you have sex, and go for regular STI testing even if neither you nor your partner(s) have symptoms.
Let partners know about positive test results immediately so you can both get treated before infecting others.
Testing every three to six months is wise if having multiple partners or casual sex. An annual screening lets those in longer-term, mutually monogamous relationships confirm everything is in order.
Make testing part of your regular health routine.
Keep Emergency Contraception as a Backup
Even individuals diligent about the proper use of barrier methods may experience mistakes such as condom breaking, cap dislodging, or forgotten spermicide doses.
 Having emergency contraceptive pills on hand provides reassurance. Emergency contraception works best the sooner you take it after a barrier mistake. Both over-the-counter options and prescription pills can prevent pregnancy if started within five days of sex.
Having emergency contraceptive pills on hand provides reassurance. Emergency contraception works best the sooner you take it after a barrier mistake. Both over-the-counter options and prescription pills can prevent pregnancy if started within five days of sex.
They’re safe to use more than once. A healthcare provider can insert an IUD for emergency contraception up to 5 days after unprotected intercourse.
Raleigh Gynecology & Wellness: Barrier Method Specialists
Raleigh Gynecology & Wellness’ team of experts has extensive experience helping patients choose the best barrier methods for safe, enjoyable intimacy.
We take the time to understand your relationships, activities, and preferences to recommend appropriate solutions and teach optimal usage techniques.
To explore the range of barrier options and get answers to all your questions, contact us today at (919) 636-6670 or schedule an online consultation and let our team offer you the judgment-free support you need so you can experience worry-free intimacy.


 An important yet lesser-known benefit of hormonal contraception is its protective effect against certain cancers. By keeping estrogen levels low and steady, it may help prevent the development of cancer-causing cells.
An important yet lesser-known benefit of hormonal contraception is its protective effect against certain cancers. By keeping estrogen levels low and steady, it may help prevent the development of cancer-causing cells. With the shot or
With the shot or 
 Thinning the Uterine Lining
Thinning the Uterine Lining Norethindrone and norgestrel – first-generation progestins similar to testosterone.
Norethindrone and norgestrel – first-generation progestins similar to testosterone.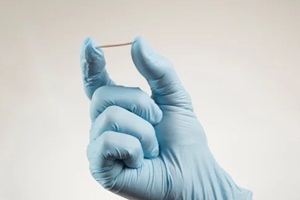
 Currently,
Currently, 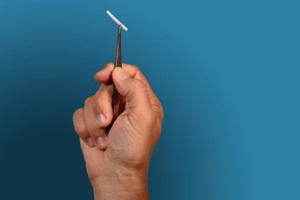 When it comes to reliable birth control, the duration and efficacy of contraceptive implants such as Nexplanon provide substantial advantages for Raleigh women focused on life goals beyond starting an immediate family.
When it comes to reliable birth control, the duration and efficacy of contraceptive implants such as Nexplanon provide substantial advantages for Raleigh women focused on life goals beyond starting an immediate family. Whether you’re focused on climbing the career ladder, finding the right relationship, or practicing self-care –
Whether you’re focused on climbing the career ladder, finding the right relationship, or practicing self-care –  Additionally, pay attention to changes in energy, productivity, or motivation in response to new pill regimens. Some ladies experience more pronounced side effects, such as exhaustion or low mood, that hinder job performance.
Additionally, pay attention to changes in energy, productivity, or motivation in response to new pill regimens. Some ladies experience more pronounced side effects, such as exhaustion or low mood, that hinder job performance. Combination birth control empowers today’s women by letting them steer their life journey, including relationships, careers, and well-being. Yet harnessing this freedom requires self-awareness plus partnership with knowledgeable doctors.
Combination birth control empowers today’s women by letting them steer their life journey, including relationships, careers, and well-being. Yet harnessing this freedom requires self-awareness plus partnership with knowledgeable doctors.