 A physician-prescribed oral contraceptive, the “minipill,” is a birth control tablet medication composed of a single hormone (progestogen) pharmaceutical compound for suppressing ovulation in women.
A physician-prescribed oral contraceptive, the “minipill,” is a birth control tablet medication composed of a single hormone (progestogen) pharmaceutical compound for suppressing ovulation in women.
Excepting compound differentiation and a few discretionary details for use, progestin pills offer the same pregnancy prevention benefits as combined pill (progestogen and estrogen) prescriptions.
The following is a breakdown of contraceptive care facts dispelling the misconceptions and myths about prescription progestin pill use.
Misconception: Oral contraceptive treatment is a hassle
Instructions for using progestin pills are daily oral ingestion at the same time for 28 days before initiating a new cycle. For maximum effectiveness, birth control tablets should be taken at the same time each day.
The pill can be used safely continuously, without a periodic break in treatment. Taking a break from oral contraceptive prescription use has the potential to lead to pregnancy.
Misconception: The pill is an ineffective form of birth control
Birth control contraceptives are 92% to 99% effective and function by inhibiting ovulation and causing a thickening of the cervix’s mucus, blocking sperm penetration during sexual intercourse. A common effect of oral contraceptive use is menstrual regulation, usually accompanied by reduced episodic cramping.
Misconception: Birth control pill contraception causes cancer
Birth control pills are proven protection from endometrial and ovarian cancer, ectopic pregnancy, and fallopian tube infections. The clinical record shows the incidence of cervical cancer associated with oral birth control use to be low.
Untreated human papillomavirus is a commonly diagnosed sexually transmitted infection (STI) connected to cervical cancer in women. Oral birth control pill use does not protect against the transmission of viral STIs.
Misconception: Taking the pill has no secondary health benefits
The health benefits of oral birth control contraception use for long-term duration are reduced incidence of anemia, cancer, ovarian cysts, and pelvic inflammatory disease.
Birth control pills are also thought to reduce menstrual bleeding, cramps, ovulatory pain, and the symptoms and onset of endometriosis and polycystic ovarian syndrome.
Myth: Birth control pill ingestion leads to short-term health problems
Some patients taking the pill may experience short-term health problems from oral contraceptive prescription drug use. Breast tenderness, headaches, and nausea are commonly cited symptoms of oral contraceptive treatment. Short-term side effects are not generally signs of severe illness and usually cease within the first two to three months of progestin pill treatment.
Myth: Oral contraception causes infertility in women
The notion that oral contraceptive care causes infertility is a myth. Depending on the patient’s age, the number of pregnancies, and the length of time taking oral contraceptive care, there may be variations in a patient’s ability to get pregnant after pill use has ceased.
Myth: The pill induces sexual promiscuity
Contraceptive care physicians reject the fallacy that oral birth control contraceptives are medically linked to increased libido, or the induction of sentience leading to sexual promiscuity. There is no evidence that oral contraceptive care is directly connected to sexual behavior, including any increase or decrease in sexual activity or performance.
Myth: Contraceptive birth control pills absorb unevenly
Concern that oral birth control pill ingestion leads to excess accumulation or uneven distribution in the body thus increasing the potential for disease and tumor growth, is false.
There is no evidence that oral contraceptives accumulate in the stomach, ovaries, and uterus. Instead, once ingested, the pill dissolves in the digestive system, causing the hormones to be absorbed by the bloodstream and metabolized by the liver and gut before discharge.
Myth: There are zero negative side-effects
 Potential side effects include breast tenderness, headaches, nausea, and weight fluctuation. Less common side effects are vascular-related conditions such as blood clots, heart attack, or stroke. There is a higher risk of cancer and vascular disorders for women over the age of 35 years who smoke.
Potential side effects include breast tenderness, headaches, nausea, and weight fluctuation. Less common side effects are vascular-related conditions such as blood clots, heart attack, or stroke. There is a higher risk of cancer and vascular disorders for women over the age of 35 years who smoke.
Myth: The pill is protection from STI risk
Birth control pills are not adequate protection against STIs (i.e., HIV/Aids). Condoms are the only proven effective birth control method for protection from STIs.
Myth: The pill leads to birth defects
There is no clinical evidence linking birth control pill use with birth defects or in vitro fetal immortality. In the rare circumstance that a pregnancy occurs during birth control pill contraceptive use should be ceased immediately with physician notice to determine the next steps for family planning and future contraceptive care.
Prescription Contraceptive Care
Raleigh Gynecology and Wellness is a licensed medical provider of gynecology and wellness services in Raleigh, North Caroline. Our healthcare practice specializes in routine care and contraceptive care, including progestin-only birth control pill prescriptions.
Find out more about family planning and pregnancy prevention by scheduling an appointment to speak with a specialist about your contraceptive care options.

 Pregnancy prevention with a birth control patch can sometimes have side effects. Find out about
Pregnancy prevention with a birth control patch can sometimes have side effects. Find out about 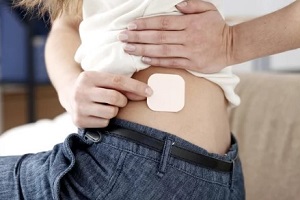
 There may be temporary side effects if discontinuing birth control patch contraceptive use. The most common side effects of going off patch use are hormonal fluctuation and a return to a normal menstrual cycle, increasing pregnancy risk. An alternative
There may be temporary side effects if discontinuing birth control patch contraceptive use. The most common side effects of going off patch use are hormonal fluctuation and a return to a normal menstrual cycle, increasing pregnancy risk. An alternative  The
The  Birth control contraceptive patch application is performed manually and is relatively simple. It is recommended to wash and dry the hands and the skin area where the patch will be placed before
Birth control contraceptive patch application is performed manually and is relatively simple. It is recommended to wash and dry the hands and the skin area where the patch will be placed before  The birth control patch method is considered one of the safest pregnancy prevention treatments available from a medical doctor.
The birth control patch method is considered one of the safest pregnancy prevention treatments available from a medical doctor.  Nexplanon is a form of
Nexplanon is a form of 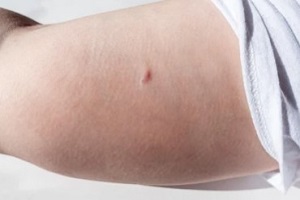 Nexplanon implants are inserted procedurally by a physician under the skin of the inside of the upper arm, followed by a topical bandage. A bandage should be worn 3 to 5 days after the procedure. Some discomfort or pressure during Nexplanon implant procedure is common.
Nexplanon implants are inserted procedurally by a physician under the skin of the inside of the upper arm, followed by a topical bandage. A bandage should be worn 3 to 5 days after the procedure. Some discomfort or pressure during Nexplanon implant procedure is common. A benefit of Nexplanon implant is that some patients experience little to no menstrual bleeding after insertion. However, there may be a risk of
A benefit of Nexplanon implant is that some patients experience little to no menstrual bleeding after insertion. However, there may be a risk of 